
Curiosity: New photos, roaming & lasers
- Rover's ChemCam will zap small Martian rock on Saturday night
- It will analyze ionized gas to identify chemical elements
- Curiosity landed in Gale Crater on August 6; scientists have been checking its systems
(CNN) -- Martian rock #N165, it's your time to shine, or glow, or whatever occurs when a hard substance gets zapped by a laser beam.
From about 10 feet away, the Mars rover Curiosity's ChemCam will take aim Saturday night at the hapless three-inch rock.
"We are going to hit it with 14 millijoules of energy 30 times in 10 seconds," Roger Wiens of Los Alamos National Laboratory told reporters.
 An updated self-portrait of the Mars rover Curiosity, showing more of the rover's deck. This image is a mosiac compiled from images taken from the navigation camera. The wall of Gale Crater, the rover's landing site, can be seen at the top of the image. The Mars rover Curiosity arrived on Mars early on August 6 and began beaming back images from the surface. See all the images as they are released here. Check out images from previous Mars missions.
An updated self-portrait of the Mars rover Curiosity, showing more of the rover's deck. This image is a mosiac compiled from images taken from the navigation camera. The wall of Gale Crater, the rover's landing site, can be seen at the top of the image. The Mars rover Curiosity arrived on Mars early on August 6 and began beaming back images from the surface. See all the images as they are released here. Check out images from previous Mars missions.  This image shows what will be the rover's first target with it's chemistry and camera (ChemCam) instrument. The ChemCam will fire a laser at the rock, indicated by the black circle. The laser will cause the rock to emit plasma, a glowing, ionized gas. The rover will then analyze the plasma to determine the chemical composition of the rock.
This image shows what will be the rover's first target with it's chemistry and camera (ChemCam) instrument. The ChemCam will fire a laser at the rock, indicated by the black circle. The laser will cause the rock to emit plasma, a glowing, ionized gas. The rover will then analyze the plasma to determine the chemical composition of the rock.  This is a close-up of the rock that will be the ChemCam's first target.
This is a close-up of the rock that will be the ChemCam's first target.  This image, cropped from a larger panorama, shows an area, near the rover's rear left wheel, where the surface material was blown away by the descent-stage rockets.
This image, cropped from a larger panorama, shows an area, near the rover's rear left wheel, where the surface material was blown away by the descent-stage rockets.  This image, with a portion of the rover in the corner, shows the wall of Gale Crater running across the horizon at the top of the image.
This image, with a portion of the rover in the corner, shows the wall of Gale Crater running across the horizon at the top of the image.  This image, taken from the rover's mast camera, looks south of the landing site toward Mount Sharp.
This image, taken from the rover's mast camera, looks south of the landing site toward Mount Sharp.  This partial mosaic from the Curiosity rover shows Mars' environment around the rover's landing site on Gale Crater. NASA says the pictured landscape resembles portions of the U.S. Southwest. The high-resolution mosaic includes 130 images, but not all the images have been returned by the rover to Earth. The blackened areas of the mosaic are the parts that haven't been transmitted yet. See more on this panaroma on NASA's site.
This partial mosaic from the Curiosity rover shows Mars' environment around the rover's landing site on Gale Crater. NASA says the pictured landscape resembles portions of the U.S. Southwest. The high-resolution mosaic includes 130 images, but not all the images have been returned by the rover to Earth. The blackened areas of the mosaic are the parts that haven't been transmitted yet. See more on this panaroma on NASA's site.  In this portion of the larger mosaic from the previous frame, the crater wall can be seen north of the landing site, or behind the rover. NASA says water erosion is believed to have created a network of valleys, which enter Gale Crater from the outside here.
In this portion of the larger mosaic from the previous frame, the crater wall can be seen north of the landing site, or behind the rover. NASA says water erosion is believed to have created a network of valleys, which enter Gale Crater from the outside here.  In this portion of the larger mosaic from the previous frame, the crater wall can be seen north of the landing site, or behind the rover. NASA says water erosion is believed to have created a network of valleys, which enter Gale Crater from the outside here.
In this portion of the larger mosaic from the previous frame, the crater wall can be seen north of the landing site, or behind the rover. NASA says water erosion is believed to have created a network of valleys, which enter Gale Crater from the outside here.  Two blast marks from the descent stage's rockets can be seen in the center of this image. Also seen is Curiosity's left side. This picture is a mosaic of images taken by the rover's navigation cameras.
Two blast marks from the descent stage's rockets can be seen in the center of this image. Also seen is Curiosity's left side. This picture is a mosaic of images taken by the rover's navigation cameras.  A color image from NASA's Curiosity rover shows the pebble-covered surface of Mars. This panorama mosaic was made of 130 images of 144 by 144 pixels each. Selected full frames from this panorama, which are 1,200 by 1,200 pixels each, are expected to be transmitted to Earth later.
A color image from NASA's Curiosity rover shows the pebble-covered surface of Mars. This panorama mosaic was made of 130 images of 144 by 144 pixels each. Selected full frames from this panorama, which are 1,200 by 1,200 pixels each, are expected to be transmitted to Earth later.  A panoramic photograph shows the Curiosity rover's surroundings at its landing site inside Gale Crater. The rim of Gale Crater can be seen to the left, and the base of Mount Sharp is to the center-right.
A panoramic photograph shows the Curiosity rover's surroundings at its landing site inside Gale Crater. The rim of Gale Crater can be seen to the left, and the base of Mount Sharp is to the center-right.  A partial view of a 360-degree color panorama of the Curiosity rover's landing site on Gale Crater. The panorama comes from low-resolution versions of images taken Thursday, August 9, with a 34-millimeter mast camera. Cameras mounted on Curiosity's remote sensing mast have beamed back fresh images of the site.
A partial view of a 360-degree color panorama of the Curiosity rover's landing site on Gale Crater. The panorama comes from low-resolution versions of images taken Thursday, August 9, with a 34-millimeter mast camera. Cameras mounted on Curiosity's remote sensing mast have beamed back fresh images of the site.  NASA's Curiosity rover took this self-portrait using a camera on its newly deployed mast.
NASA's Curiosity rover took this self-portrait using a camera on its newly deployed mast.  A close-up view of an area at the NASA Curiosity landing site where the soil was blown away by the thrusters during the rover's descent on August 6. The excavation of the soil reveals probable bedrock outcrop, which shows the shallow depth of the soil in this area.
A close-up view of an area at the NASA Curiosity landing site where the soil was blown away by the thrusters during the rover's descent on August 6. The excavation of the soil reveals probable bedrock outcrop, which shows the shallow depth of the soil in this area.  This color full-resolution image showing the heat shield of NASA's Curiosity rover was obtained during descent to the surface of Mars on Monday, August 13. The image was obtained by the Mars Descent Imager instrument known as MARDI and shows the 15-foot diameter heat shield when it was about 50 feet from the spacecraft.
This color full-resolution image showing the heat shield of NASA's Curiosity rover was obtained during descent to the surface of Mars on Monday, August 13. The image was obtained by the Mars Descent Imager instrument known as MARDI and shows the 15-foot diameter heat shield when it was about 50 feet from the spacecraft.  This first image taken by the Navigation cameras on Curiosity shows the rover's shadow on the surface of Mars.
This first image taken by the Navigation cameras on Curiosity shows the rover's shadow on the surface of Mars. 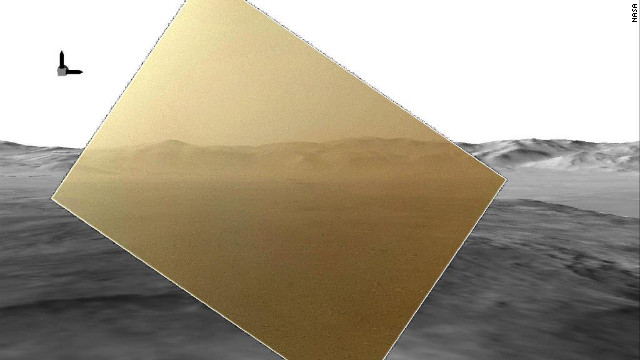 The color image captured by NASA's Mars rover Curiosity on Tuesday, August 7, has been rendered about 10% transparent so that scientists can see how it matches the simulated terrain in the background.
The color image captured by NASA's Mars rover Curiosity on Tuesday, August 7, has been rendered about 10% transparent so that scientists can see how it matches the simulated terrain in the background.  This image comparison shows a view through a Hazard-Avoidance camera on NASA's Curiosity rover before and after the clear dust cover was removed. Both images were taken by a camera at the front of the rover. Mount Sharp, the mission's ultimate destination, looms ahead.
This image comparison shows a view through a Hazard-Avoidance camera on NASA's Curiosity rover before and after the clear dust cover was removed. Both images were taken by a camera at the front of the rover. Mount Sharp, the mission's ultimate destination, looms ahead.  The four main pieces of hardware that arrived on Mars with NASA's Curiosity rover were spotted by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment camera captured this image about 24 hours after landing.
The four main pieces of hardware that arrived on Mars with NASA's Curiosity rover were spotted by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment camera captured this image about 24 hours after landing.  This image is a 3-D view in front of NASA's Curiosity rover. The anaglyph was made from a stereo pair of Hazard-Avoidance Cameras on the front of the rover. Mount Sharp, a peak that is about 3.4 miles high, is visible rising above the terrain, though in one "eye" a box on the rover holding the drill bits obscures the view.
This image is a 3-D view in front of NASA's Curiosity rover. The anaglyph was made from a stereo pair of Hazard-Avoidance Cameras on the front of the rover. Mount Sharp, a peak that is about 3.4 miles high, is visible rising above the terrain, though in one "eye" a box on the rover holding the drill bits obscures the view.  This view of the landscape to the north of NASA's Mars rover Curiosity was acquired by the Mars Hand Lens Imager on Monday afternoon on the first day after landing.
This view of the landscape to the north of NASA's Mars rover Curiosity was acquired by the Mars Hand Lens Imager on Monday afternoon on the first day after landing.  This view of the landscape to the north of NASA's Mars rover Curiosity was acquired by the Mars Hand Lens Imager on Monday afternoon, the first day after landing.
This view of the landscape to the north of NASA's Mars rover Curiosity was acquired by the Mars Hand Lens Imager on Monday afternoon, the first day after landing.  This is one of the first pictures taken by Curiosity after it landed. It shows the rover's shadow on the Martian soil.
This is one of the first pictures taken by Curiosity after it landed. It shows the rover's shadow on the Martian soil.  Another of the first images taken by the rover. The clear dust cover that protected the camera during landing has popped open. Part of the spring that released the dust cover can be seen at the bottom right, near the rover's wheel.
Another of the first images taken by the rover. The clear dust cover that protected the camera during landing has popped open. Part of the spring that released the dust cover can be seen at the bottom right, near the rover's wheel.  This image shows Curiosity's main science target, Mount Sharp. The rover's shadow can be seen in the foreground. The dark bands in the distances are dunes.
This image shows Curiosity's main science target, Mount Sharp. The rover's shadow can be seen in the foreground. The dark bands in the distances are dunes.  Another of the first images beamed back from NASA's Curiosity rover on August 6 is the shadow cast by the rover on the surface of Mars.
Another of the first images beamed back from NASA's Curiosity rover on August 6 is the shadow cast by the rover on the surface of Mars.  NASA's Mars Curiosity Rover, shown in this artist's rendering, touched down on the planet on August 6.
NASA's Mars Curiosity Rover, shown in this artist's rendering, touched down on the planet on August 6.  Photos: Mars rover Curiosity
Photos: Mars rover Curiosity A millijoule is 1/1000th of a joule, which is way too complicated to explain here. Suffice to say, it should get the job done.
ChemCam, short for Chemistry and Camera, will analyze the resulting glowing, ionized gas in an effort to identify chemical elements in the rock.
Scientists say it will be the first time such a powerful laser has been used on another planet. The laser works in conjunction with a telescope.
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory said Friday that Curiosity's first driving destination will be Glenelg, about 1,300 feet from the rover's landing site.
"We had a bunch of strong contenders. It is the kind of dilemma planetary scientists dream of, but you can only go one place for the first drilling for a rock sample on Mars," said project scientist John Grotzinger. "That first drilling will be a huge moment in the history of Mars exploration."
The mobile science lab touched down on Mars early on August 6 and has been beaming back images of the surface of Gale Crater ever since.
The rover's primary target is Mount Sharp, a peak about 8 kilometers (5 miles) away. But moving about a football field a day, with lengthy stops, it could take nearly a year to reach the slopes at the base of the mountain.


























No comments:
Post a Comment